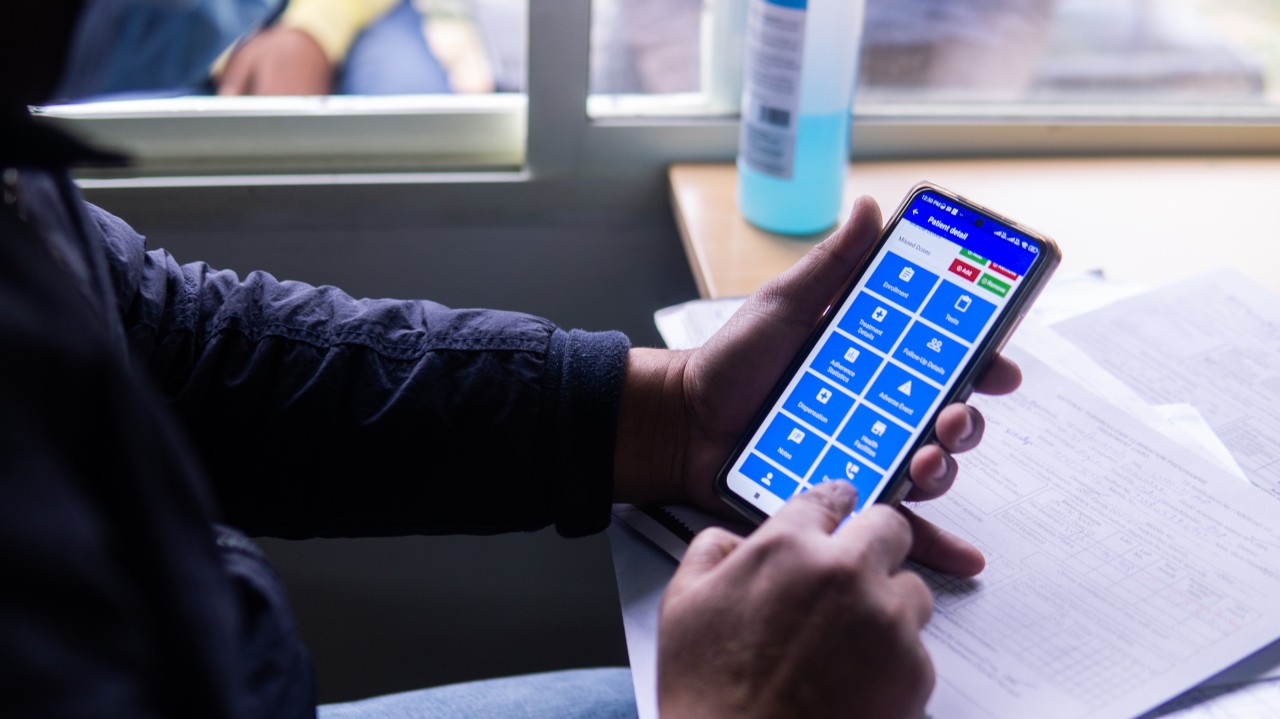
Rapidly scaling screening, testing and quarantine has shown to be an effective strategy to combat the COVID-19 pandemic. We consider the application of deep learning techniques to distinguish individuals with COVID from non-COVID by using data acquirable from a phone. Using cough and context (symptoms and meta-data) represent such a promising approach. Several independent works in this direction have shown promising results. However, none of them report performance across clinically relevant data splits. Specifically, the performance where the development and test sets are split in time (retrospective validation) and across sites (broad validation). Although there is meaningful generalization across these splits the performance significantly varies (up to 0.1 AUC score). In addition, we study the performance of symptomatic and asymptomatic individuals across these three splits. Finally, we show that our model focuses on meaningful features of the input, cough bouts for cough and relevant symptoms for context.